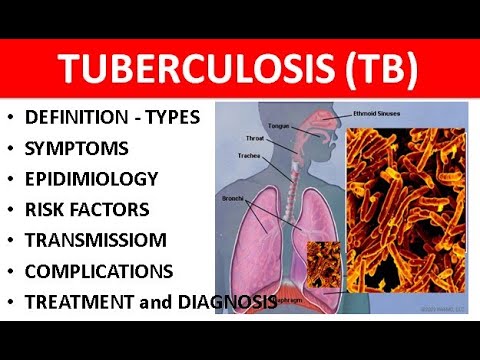
Tuberculosis (TB) – Symptoms and Treatment
- 12 Sep 2025
- 0 Comments
- Tuberculosis, TB Control, Lung Health
Tuberculosis (TB) – Symptoms, Treatment, and Causes in Pakistan
Introduction
Tuberculosis (TB) is one of the oldest known infectious diseases and still remains a major public health challenge across the world. Caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis, TB primarily affects the lungs but can also spread to other parts of the body such as the kidneys, spine, and brain. Despite being preventable and treatable, TB continues to claim thousands of lives every year.
In Pakistan, TB is a serious health concern. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), Pakistan is among the countries with the highest burden of tuberculosis. Poverty, overcrowding, lack of awareness, and limited healthcare access are major reasons behind the rising number of TB cases.
Symptoms of Tuberculosis (TB)
TB develops slowly, and many people mistake its early signs for common illnesses. Recognizing the symptoms at the right time is critical for treatment.
Common symptoms include:
-
Persistent cough lasting more than 2–3 weeks
-
Coughing up blood or mucus
-
Chest pain and difficulty breathing
-
Unexplained weight loss
-
Loss of appetite
-
Fever and night sweats
-
Fatigue and weakness
If left untreated, TB can spread within the body and to others through coughing or sneezing.
Treatment of Tuberculosis
The good news is that TB is curable with the right treatment. Doctors usually prescribe a combination of antibiotics over a period of 6 to 9 months.
Treatment methods include:
-
Drug Therapy: Medicines like isoniazid, rifampicin, ethambutol, and pyrazinamide are commonly used.
-
Directly Observed Treatment, Short-Course (DOTS): A strategy recommended by WHO where healthcare workers ensure patients complete their medication properly.
-
Supportive Care: Proper nutrition, rest, and regular follow-ups help the recovery process.
Stopping treatment midway or irregular use of medicines can cause drug-resistant TB, which is much harder to treat and a growing threat in Pakistan.
Causes of TB Spread in Pakistan
Several factors contribute to the high TB rate in Pakistan:
-
Overcrowding and Poverty: Many people live in congested areas with poor ventilation, making TB spread faster.
-
Lack of Awareness: People often ignore early symptoms, delaying diagnosis and treatment.
-
Weak Healthcare Access: Rural areas lack proper medical facilities, leading to untreated cases.
-
Malnutrition: Poor diets weaken the immune system, increasing vulnerability.
-
Co-infections: Patients with HIV or diabetes are more likely to develop TB.
-
Incomplete Treatment: Many patients stop taking medicines once they feel better, leading to drug resistance.
Conclusion
Tuberculosis remains a major health challenge in Pakistan, but it is preventable and curable if treated on time. Recognizing early symptoms, seeking medical help quickly, and completing the full course of treatment are the keys to fighting TB.
The government and healthcare organizations must also strengthen awareness campaigns, improve healthcare facilities, and ensure access to free treatment programs. At the same time, individuals must play their part by maintaining good hygiene, supporting patients, and spreading awareness.